What are the Causes, and Treatments of Kidney Pain?
In this article, we are going to discuss kidney pain, the difference between kidney pain and Back pain, causes of kidney pain, symptoms, and treatment.
What are the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments of Kidney Pain?
You have two kidneys, one on each side of your spine, located behind your ribs in the back of your abdomen. The pain you feel in your upper back or sides may be due to kidney pain or not. It may be due to back pain.
However, having pain in the back or sides may not mean you have kidney problems. In contrast to back pain, kidney pain is generally felt deeper and higher up in the spine. The pain can also spread to other areas, such as the abdomen or groin. If only one kidney is affected, pain may be felt only on one side, or if both kidneys are damaged, both sides.
In this article, we are going to discuss kidney pain, the difference between kidney pain and Back pain, causes of kidney pain, symptoms, and treatment.
What are the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments of Kidney Pain?
You have two kidneys, one on each side of your spine, located behind your ribs in the back of your abdomen. The pain you feel in your upper back or sides may be due to kidney pain or not. It may be due to back pain.
However, having pain in the back or sides may not mean you have kidney problems. In contrast to back pain, kidney pain is generally felt deeper and higher up in the spine. The pain can also spread to other areas, such as the abdomen or groin. If only one kidney is affected, pain may be felt only on one side, or if both kidneys are damaged, both sides.
The kidneys hurt, but why?
What are the symptoms of kidney pain?
Pain in the kidneys: what is the treatment?
The kidneys hurt, but why?
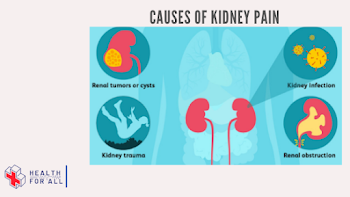
· Stones in the kidney
· Infection of the urinary tract
· Pyelonephritis
· The polycystic kidneys
· Injury or trauma
· Cancer of the kidney (renal)
The following details provide information related to kidney pain causes:
Minerals or chemical wastes can build up inside the body and lead to kidney stones. There are a variety of sizes of stones, even smaller than sand grains and larger than pearls. Smaller ones may pass through the body. Large stones, on the other hand, can become stuck in the urinary tract and prevent the flow of urine. A painful outcome can be expected either way.
Infection of the urinary tract:
Bacteria deposited in the urinary tract after urinating can cause an infection. This condition can cause general fatigue, fever, cloudy urine, and painful urination.
Pyelonephritis:
Bacteria from a bladder infection can spread to the kidneys, causing a kidney infection called pyelonephritis. Diabetics and people with a blocked urinary tract are more susceptible to kidney infections. The kidneys may eventually become permanently damaged if urine flows backward into the bladder after repeated infections and malfunctioning of the urinary tract.
The polycystic kidneys:
Specifically, the development of fluid-filled sacs (cysts) inside the kidneys as a result of inheritable factors. Eventually, the kidneys may become engorged because of cysts and they may no longer function.
Injury or trauma:
Getting hit hard in the kidney area (such as in contact sports or in an accident) can cause a laceration or other injuries to the kidney. It has also been reported that such incidents may disrupt the kidneys' blood flow. Trauma to the kidneys can cause acute (sudden) kidney failure.
Cancer of the kidney (renal):
The most common type of kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma. People in their 60 s or 70 s are usually affected by it, and those under the age of 50 are seldom affected by it. If they occur, symptoms consist of bloody urine, constant pain in the back or side just below the ribs, and a lump or swelling in the side.
What are the symptoms of kidney pain?
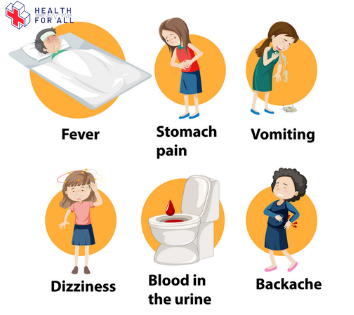
The following symptoms are associated with kidney pain:
- Chills and fever
- Bloody urine
- Urination frequently
- Feeling nauseated and vomiting
- The pain spreads to your groin
- An uncomfortable burning sensation after urinating
- An infection of the urinary tract recently.
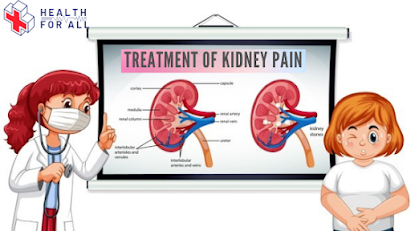
Pain in the kidneys: what is the treatment?
- Urinalysis: Identifies blood, excess white blood cells (which could indicate infection), proteins, and chemicals that can indicate kidney disease.
- Imaging tests: An ultrasound or a CT (computed tomography) scan can provide information about the kidneys and urinary tract's physical structure, identify stones, and check the blood flow.
It is only when you and your doctor are fully aware of what is causing your pain that you can receive the right treatment.
Some related articles:
Kidney Stones Causes, symptoms, and treatment
Can peach fuzz turn into a beard?




Nice work
ReplyDelete